What is fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia, also called fibrositis, is a chronic,
widespread pain in muscles and soft tissues surrounding the joints
throughout the body, accompanied by fatigue. The disease is fairly
common, affecting approximately 2 percent of the US population (three
to six million Americans).
Although its symptoms are similar to other joint diseases, such as arthritis, fibromyalgia is actually a form of soft tissue or muscular rheumatism that causes pain in the muscles and soft tissues. Fibromyalgia is more prevalent in women of childbearing age.
Fibromyalgia is one of several pain syndromes included in the classification of musculoskeletal pain syndrome (MSPS), or pain amplification syndrome.
What causes or triggers fibromyalgia?
Although the cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, researchers
believe there may be a link with sleep disturbance, psychological
stress, or immune, endocrine, or biochemical abnormalities.
Fibromyalgia mainly affects the muscles and the points at which the
muscles attach to the bone (at the ligaments and tendons).
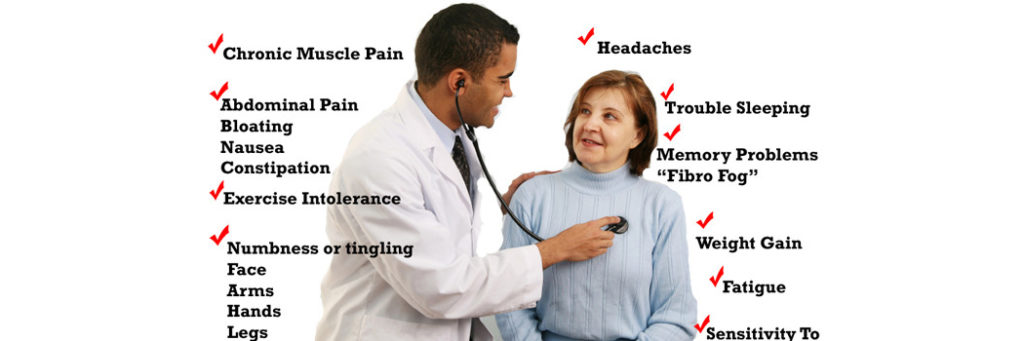
What are the symptoms of fibromyalgia?
Pain is the most common and chronic symptom of
fibromyalgia. Pain may begin in one area of the body, such as the neck
and shoulders, but eventually the entire body may become affected. The
pain ranges from mild to severe and may be described as burning,
soreness, stiffness, aching, or gnawing pain. Fibromyalgia usually is
associated with characteristic tender spots of pain in the muscles. The
following are other common symptoms of fibromyalgia. However each
individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
- moderate to severe fatigue
- decreased exercise endurance
- sleep problems at night
- depressed mood
- anxiety
- headaches
- abdominal pain and bloating
- diarrhea, alternated with constipation
- urinary urgency
The symptoms of fibromyalgia may resemble other medical conditions or problems. Always consult your physician for a diagnosis.
How is fibromyalgia diagnosed?
There are no laboratory tests that can confirm a diagnosis
of fibromyalgia. Instead, diagnosis is usually based on reported
symptoms.
Treatment for fibromyalgia:
Specific treatment for fibromyalgia will be determined by your physician based on:
- your age, overall health, and medical history
- extent of the condition
- your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, and therapies
- expectation for the course of the condition
- your opinion or preference
Although there is no cure for fibromyalgia, the disease can often be successfully managed with proper treatment, as fibromyalgia does not cause damage to tissues. Treatment may include: is one of the most popular medications most commonly prescribed by doctors to treat a unique type of pain in fibromyalgia. Therefore, more and more people are interested in It has already been proven that opioids like tramadol are addictive and it is very dangerous to take them without a doctor’s prescription.
- anti-inflammatory medications (to relieve pain and improve sleep)
- exercise and physical therapy (to stretch muscles and improve cardiovascular fitness)
- relaxation techniques
- heat treatments
- occasional cold applications
- massage



